Dynamic Programming
- Like Divide-and-Conquer, Dynamic Programming is a design technique of algorithms.
Longest Common Subsequence(LCS)
- LCS is a famous example of a problem that could be solved using DP.
- Given two sequence x[1, ... , m] and y[1, ... , n], the goal is to find the longest subsequence common to both.

- A naive approach is to check every subsequence of x to se if it is also a subsequence of y.
- There exists 2^m subsequence in x, and checking each of them exist in y requires n search, resulting O(n*(2^m)) run time.
- The key idea to apply DP to this problem is to look at the length of a LCS.
- We should extend the algorithm to find the solution itself.
- Let us denote c[m,n] = | LCS(x,y) | where m and n is the range in which we inspected for LCS.
- The recurrence could be derived as the figure below.

- The reason why we could apply DP to this problem is because of the property DP holds.
- DP could be applied if an optimal solution to a problem contains optimial solutions to subproblems (Optimal Substructure).
e.g. If z= LCS(x,y), then any prefix of z is an LCS of a prefix of x and a prefix of y.

- In the naive approach we do not consider if same subproblem occurs.
- This means we're solving subproblems that was already solved.
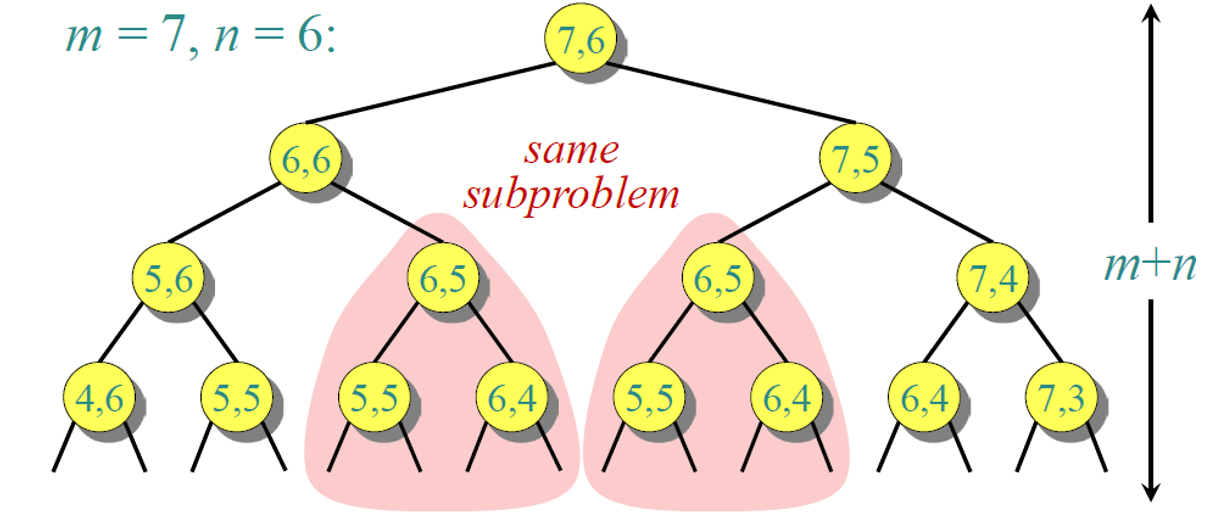
- The technique of using the solution to the already solved subproblem is called Memoization.
- Another property that is required to apply DP to a problem is Overlapping Subproblems; a recursive solution contains a small number of distinct subproblems repeated many times.

Assembly Line Scheduling
- Assembly Line Scheduling is another type of problem that could be solved efficiently via DP.

- Using Brute force, we should enumerate all possibilities of selecting stations leading to O(2^n) run time.
- Finding the optimal solution to the problem "Fastest way through S1,j" has the same optimal solution with the subproblems, "Fastest way through S1,j-1 or S2,j-1".
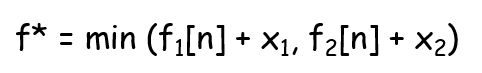
Matrix Chain Multiplication
- The given task is to choose the order in which to compute the matrix multiplication.

- The figure above shows that choosing the order to calculate matrix multiplication matters a lot to the overall number of operations.
- A similar problem occurs for SQL join queries.
- Exhaustively checking all possible parenthesizations is not efficient.
- Let us define m[i,j] as the minimum number of multiplications needed to compute Ai,...,j .

- We could derive the recurrence as the figure above.
- Overall computation would take O(N^3).
Knapsack Problem
- Knapsack Problem is another type of problem that could be solved using DP.
- K is the knapsack capacity limit, and v, w are value and weight of each product.
- Our goal is to get the maximum value when an upper bound for the total weight is given.
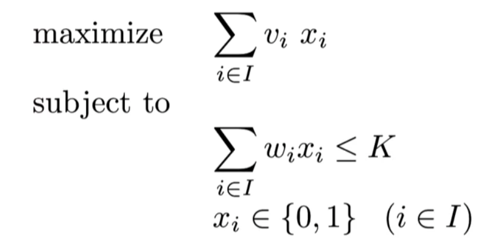
- Let us define V[i,w] as the maximum value when products up to i with maximum weight of w is given.
- The total amount of runtime would be O(NW).
'Algorithms & ICPC' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Greedy (0) | 2021.10.17 |
|---|---|
| Order Statistics (0) | 2021.10.13 |
| Trees (0) | 2021.10.13 |
| Linear Sorting (0) | 2021.09.27 |



